소식
- 일반
- (보도기사)모션컴퓨팅랩 이성희 교수님/박사과정 김미경, 살 떨림 재현 기술 개발하여 CG·애니메이션에 활용
- 관리자 |
- 2017-08-18 17:21:18|
- 1055
- 2017-08-18 17:21:18|
살 떨림 재현 기술 개발... CG·애니메이션에 활용(Motion Computing Lab develops a technology that recreates vibration of soft tissue)
KAIST(총장 신성철)가 인간의 살 떨림 모션을 손쉽게 재현할 수 있는 기술을 개발했다. 컴퓨터그래픽(CG)이나 애니메이션에 활용하면 훨씬 역동성 있고 실감나는 영상을 얻을 수 있다.
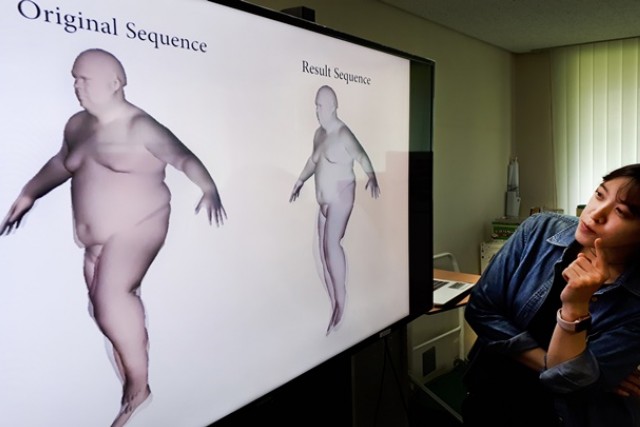
KAIST는 이성희 문화기술대학원 교수팀이 인체가 움직이는 과정에서 발생하는 살의 떨림을 기존 방식보다 쉽고 정밀하게 구현하는 '관찰 기반 물리 인체 캐릭터 시뮬레이션' 기술을 개발했다고 13일 밝혔다.
인간의 살 떨림을 영상으로 재현하기 위해서는 그동안 카메라 여러 대로 대상을 캡처하거나 물리 연산을 이용해 시뮬레이션을 했다. 그러나 이 같은 방법은 뚜렷한 단점이 있어 양질의 영상을 얻기 어려웠다. 캡처 방식은 인체 관절 움직임의 경우 실제로 담을 수 있지만 살 떨림 재현이 제한돼 역동적 떨림을 구현하기 어려웠다. 직접 카메라로 촬영한 것 외에 다양한 영상을 얻을 수도 없었다.
기존 시뮬레이션 방식은 상대적으로 범용성이 뛰어나고 미세한 살 떨림을 구현할 수 있지만 영상을 얻기 위해서는 많은 시간과 컴퓨팅 파워가 필요했다. 간단한 캐릭터나 신체 일부 모습 재현에 주로 쓰였다.
연구팀은 여기에 캡처한 인체 영상과 시뮬레이션의 결과 값을 비교하고, 물성 값을 자동으로 부여하는 알고리즘을 적용했다. 서로 다른 결과 값의 격차를 측정, 자동으로 오차를 줄이는 역할을 한다. 이 결과 인체 전체를 시뮬레이션하는 것에 비해 4배 빠른 속도로 살 떨림 영상을 얻을 수 있다. 고속으로 움직이는 다양한 인체 영상에 실제와 같은 살 떨림 효과를 넣는 것도 가능해진다.
KAIST는 이 기술을 지난 1일 '시그래프(SIGGRAPH) 학회'에서 소개했다. 시각 기술 관련 세계 최고 수준의 학회다.

연구팀은 내년에 '기가코리아 정부 과제 사업'에 참여, 기업과 기술 상용화를 위한 후속 연구에 나설 계획이다.
이상희 교수는 “캡처와 시뮬레이션 방식을 융합해 더욱 역동적인 살 떨림 영상을 손쉽게 얻는 기술을 개발했다”면서 “영상 콘텐츠 사실성을 높이고 가치를 더하는 기반 기술이 될 것”이라고 말했다.
참조: 전자신문 2017.8.13
원본보기: http://www.etnews.com/20170811000293
KAIST (Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology, President Shin Sung-chul) has developed a technology that can easily recreate a motion of vibration of human soft tissue. If this technology is applied to CG (Computer Graphic) or animations, one can obtain images that are more realistic and dyanmic.
KAIST announced on the 13th that a research team led by Professor Lee Sung-hee of The Graduate School of Culture Technology has developed ‘observation-based physical body character simulation’ technology that implements vibration of soft tissue that occurs when there is movement of a human body easier and more accurate than current methods.
Until now one had to either capture a subject with many cameras or use physical calculations in order to recreate vibration of human soft tissue through images. However it was difficult to obtain images with good quality as these methods have clear flaws. Although capturing a subject with many cameras can actually capture movements of human joints, it was difficult to implement dynamic vibrations as there were limitations in recreating vibration of soft tissue. It could not also capture other variety of images except for the subjects that are directly captured with cameras.
Although current simulation methods have relatively excellent versatility and can implement accurate vibration of soft tissue, many hours and computing power were needed in order to obtain images. They were mostly used for simple characters or recreation of certain body parts.
Research team compared results of simulation and images of a human body that are captured and applied an algorithm that automatically gives property value. This algorithm measures difference in values of different results and automatically reduces any errors. As a result, research team was able to obtain images of vibration of soft tissue at a speed that was four times faster than simulating entire human body. It is also possible to apply effect of vibration of soft tissue that is like actual vibration of soft tissue to variety of images of human bodies that are moving at fast speed.
KAIST introduced this technology at ‘SIGGRAPH’, which is the world’s highest-level conference for visual technologies, on the 1st of this month.
Research team is planning to participate in South Korean Government’s GiGA Korea project in 2018 and carry out follow-up research in order to commercialize technologies and companies.
“We have developed a technology that can easily obtain images of more dynamic vibration of soft tissue by combining capturing and simulation methods.” said Professor Lee Sang-hee. “It will be a technology that adds values and increases reality of images.”
| 첨부파일 |
|---|
- 이전
- (보도기사) 박사과정 이정섭(지도교수:이성희) 대전의 젊은 예술가들을 만나다
- 2017-07-31